Any difficulty of differential diagnosis can be solved easily with the help of laboratory tests.
 ?-fetoprotein
?-fetoprotein
The most common sign of AT is the high rate of ?-fetoprotein in the blood after the age of 2 years. The ?-fetoprotein is a protein found in the serum of the fetus that is not produced any more, in principle, two weeks after birth. After, finding an abnormal rate may indicate cancer but also a neurological disease, including ataxia telangiectasia.
Immunoglobulins
Low levels of antibodies ( IgA, IgG and/or IgE ) can also help guide the diagnosis. However, these data indicating a disorder of the immune system vary from one patient to another and are not always abnormal in patients with AT.
Karyotype
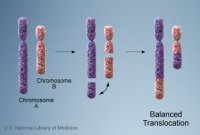 The presence of spontaneous chromosome breaks and rearrangements in lymphocytes (white blood cells) and skin fibroblasts (constituents of the structure of the skin), although they are not always present, is another important laboratory sign to look specifically in AT. Similarly, the detection of translocation (exchange) of chromosomal material between chromosomes 7 and 14 is suggestive.
The presence of spontaneous chromosome breaks and rearrangements in lymphocytes (white blood cells) and skin fibroblasts (constituents of the structure of the skin), although they are not always present, is another important laboratory sign to look specifically in AT. Similarly, the detection of translocation (exchange) of chromosomal material between chromosomes 7 and 14 is suggestive.
Study of the ATM gene
Now that the ATM gene has been identified, it is possible to confirm the diagnosis by trying to detect mutations in the patient's DNA. The team of Professor Dominique Stoppa-Lyonnet helped to highlight the entire ATM gene mutations in all patients identified in France, providing a unique knowledge base in the world.