Telangiectasias (spider veins) are a visible but mild sign of Ataxia telangiectasia.
Other cutaneous signs may appear during the disease. They can both be symptoms useful for diagnosis but also dangers.
Telangiectasia
In "Ataxia Telangiectasia", there is also "telangiectasia".
 Definition
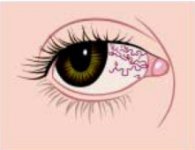
DefinitionTelangiectasia stands for an abnormal vascular expansion in size and permanence. It is red and forms a thin , tortuous line, often as an arborization or network and is most visible in the eye. Differentiation is harder on the skin as it has to be differentiated from normal dermal vessel seen by transparency.
In AT
Telangiectasia appear from 3 years, sometimes much later in adolescence, first in the eyes, and then inside the ears, eyelids, the bend of the arms and the creases of the knees. They have no effect on vision.
We do not know exactly the process of formation of these telangiectasias, except that they are almost certainly a consequence of the ATM protein deficiency on the cell cycle of vascular walls.
Treatment
There is no substantive treatment to cure them. If there is an aesthetic discomfort , they can be treated by local destruction by electrocoagulation or vascular lasers. The results are good overall, but less satisfactory for telangiectasias of the lower limbs.
Finally, it is not stated in the eye and anyway, the alteration of cells resulting from these treatments do not seem appropriate in the specific case of AT.
Non-infectious granulomas
The granuloma is initially small, consisting of propagation, within a tissue, of a number of cells. These cells have defense capabilities and come from white blood cells (monocytes type). This is primarily macrophages that evolve into epithelioid cells and eventually form giant cells with multiple nuclei. Microscopic examination shows that they are surrounded by a wreath of white blood cells: lymphocytes.
The granuloma is most often due to a localized reaction after penetration of a germ (infectious agent). On the skin, the starting point may be only a small pustule, the site of injection of a vaccine or a local trauma as the penetration of a foreign body. The granuloma is sometimes unexplained.
As it isn't well known, the granuloma can't be treated easily. Usually, ointments are used with the initial goal of stabilizing. Skin grafts were attempted in areas heavily affected, but without success. Only the use of an intravenous anti-TNF agent (biotherapy with anti-inflammatory effect) showed some effectiveness, but there are sometimes serious side effects and reduced immunity. Thus, in the case of a patient with AT, it has to be handled with care.
Leuco melano dermis: pigmentation disorder
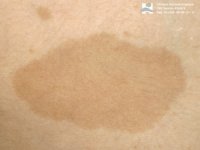 A pigmentation disorder (coloration of the skin)is sometimes observed in some patients characterized simultaneously by an excess of color (coffe stains) and a default of color (very pale areas). We talk about leuco melano dermis.
A pigmentation disorder (coloration of the skin)is sometimes observed in some patients characterized simultaneously by an excess of color (coffe stains) and a default of color (very pale areas). We talk about leuco melano dermis. If AT is not the only disease that is concerned with this peculiarity, this disorder is part of the bundle of symptoms that characterizes it.
Progeria type atrophy
This is due to the process of cell reproduction described in section "ATM: DNA controller" : the absent ATM protein no longer controls the cellular repair, allowing damaged skin cells to reproduce.
The skin becomes fragile and provides a more conducive ground to development of other conditions.
Eczema
Seborrhea
Some skin disorders are caused by excess of sebum, mainly in young individuals (acne or dermatitis). Seborrhea can also occur in some neurological diseases (Parkinson, AT) or when there is an excess of hormones (estrogen).
Abnormal sensitivity to radiation
However, this is the heart of the target of the repair process in which the ATM protein is involved (see ATM: DNA controller" ). If the protein is inactive, the cells affected by radiation, therefore altered, can reproduce with their degeneration. Thus, the risk of cancer is increased.
More than a treatment, one must focus on prevention (see Radiation).
Hirsutism
Premature gray hair
 Indeed, the cells responsible for hair color called melanocytes (or MSC) are present initially in the form of stem cells in the hair follicle (the base of the hair). These "baby cells" CSM (or MSCs) differentiate progressively into functional cells and follow the growth of hair in normal times.
Indeed, the cells responsible for hair color called melanocytes (or MSC) are present initially in the form of stem cells in the hair follicle (the base of the hair). These "baby cells" CSM (or MSCs) differentiate progressively into functional cells and follow the growth of hair in normal times. A team of Japanese researchers has shown that if these MSCs undergo aggression, chemical or radiation, which irreparably damaged their DNA, they do not necessarily die: they can still make their maturation, but remained trapped in the follicle. Not following the growing hair, they do not stain it anymore: it turns white.
These attacks take place constantly and in very large numbers. And guess who controls the repair of the MSCs, destroys them or let them turn in the wrong place? The ATM protein of course! If it is absent, the degradation occurs more rapidly.
This finding confirms the suspicions and observations: ATM is one of the molecules of aging.
Trush
 It is sometimes difficult to detect an immune deficiency in a young child. Some recurrent infections may provide a lead to the diagnosis as thrush.
It is sometimes difficult to detect an immune deficiency in a young child. Some recurrent infections may provide a lead to the diagnosis as thrush. Thrush is an infection that occurs in the oral mucosa, tongue, pharynx, sometimes the nails and skin folds. It is caused by a fungus, candida albicans, and develops when the defenses of the body are low. It is favored by antibiotics or acidity as in a reflux. It is more common among infants, the elderly but also the immune deficients.
Conclusion
Moreover, the now proven effects on aging of ATM may open a new field of research, particularly for the cosmetics industry and therefore, in the knowledge of the gene.